Methodological approach for the use of agricultural transformation losses based on lean manufacturing: Case Study on a coffee farm in Colombia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2024.028Keywords:
lean agriculture, agricultural losses, process improvement, transformation process, compostAbstract
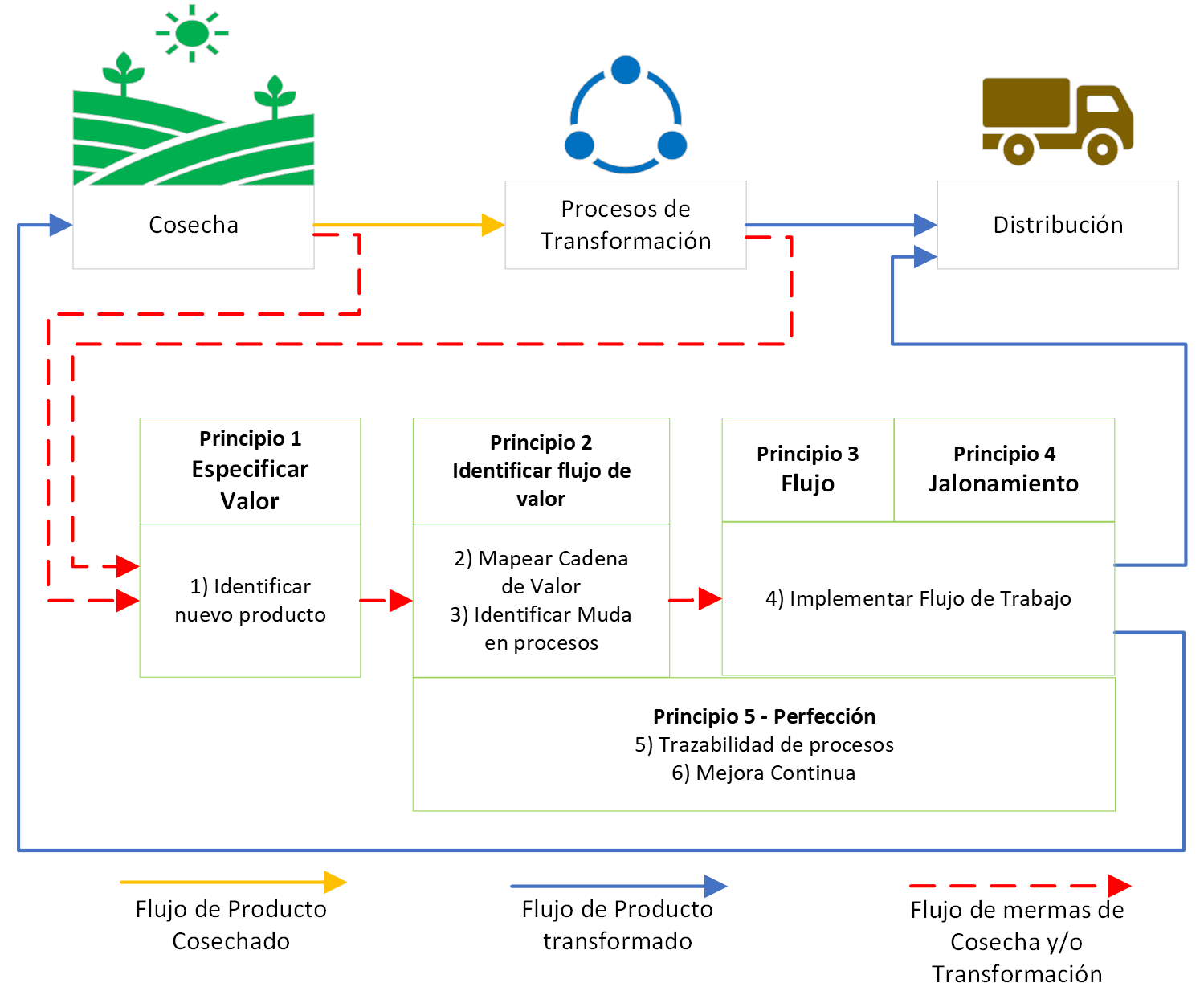
Improvements in production systems that use the lean manufacturing approach known as “Lean” have the objective of eliminating or reducing waste or process inefficiencies (muda). This approach is increasingly adopted by different industrial sectors, including agriculture. Although Lean improvements are traditionally applied to existing processes from cultivation to distribution, opportunities to intervene in processing wastes (losses) are left aside. This article presents a methodological approach framed in five Lean principles, made up of six activities aimed at the design of new processes that make use of the losses generated by harvesting and agricultural transformation. The methodological approach is applied in a Colombian coffee farm where parchment coffee transformation processes are developed. A parallel losses composting process is designed that transforms defective, green, overripe beans, coffee pulp, mucilage and husk. The results show that by applying the methodological approach on the coffee farm, a level of losses transformation of 86% is achieved. Molting is also reduced for both the current parchment coffee production line and the composting line to 35% and 50% respectively. The main reductions are reprocessing and waiting times. Finally, a 30.3% reduction is obtained in the time of activities that do not add value, making both the current and proposed processes more efficient and with better delivery times.
References
Andersson, K., Eklund, J., & Rydberg, A. (2020). Lean Inspired development work in agriculture: Implications for the work environment. Agronomy Research, 18(2), 324-345. doi.org/10.15159/AR.20.043.
Barth, H., & Melin, M. (2018). A green lean approach to global competition and climate change in the agricultural sector: A Swedish case study. Journal of cleaner production, 204, 183-192. doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.021.
Baumont, F., Forbes, H., Schaefer, D., & Milisavljevic, J. (2020). Lean Principles in vertical farming: A Case study. 53rd Conference on Manufacturing Systems. Chicago: Procedia CIRP.
Bella, I., Danusaputro, S., & Nurprihatin, F. (2024). The implementation of Lean Six Sigma approach to minimize waste at a food manufacturing industry. Journal of Engineering Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jer.2024.01.022.
Bicheno, J. (2004). The New Lean Toolbox: Towards Fast, Flexible, Flow. Buckingham, UK.: Moreton Press.
Bohorquez, W. (2019). The composting process. Bogotá, Colombia: Unisalle Editions. ISBN 978-958-5486-67-6.
Caicedo, N., Garcia, G., & Montoya, J. (2019). Towards the integration of lean principles and optimization for agricultural production systems: A conceptual review proposition. Science of Food and Agriculture, 100(2), 453-464. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10018.
Caicedo, N., Garcia, G., Montoya, J., & Ramirez, L. (2020). A planning model of crop maintenance operations inspired in lean manufacturing. Computers and electronics in Agriculture, 179, 105852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105852.
Chairany, N., Hidayatno, A., & Suzianti, A. (2022). Risk Analysis Approach to Identifying Actions that Reduce Waste for a Lean Agricultural Supply Chain. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 15(2), 350-366. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.3678.
Chavez, J., Osorio, F., Dominguez, F., Raymundo, C., & Altamirano, E. (2019). Lean production management model for SME waste reduction in the processed food sector in Peru. International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics. San Diego: Springer.
Czekala, W., Lukomska, A., Pulka, J., Bojarski, W., Pochwatka, P., Kowalczyk, A., Oniszczuk, A., & Dach, J. (2023). Waste to energy: Biogas potential of waste from coffee production and consumption. Energy, 276, 127604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127604.
FAO. (2011). Global Food Losses and Food Waste. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/3/i2697e/i2697e.pdf.
Fladkjaer, V., & Pejstrup, S. (2018). Lean in Agriculture: Create More Value with less work on the farm. Routledge. Taylor & Francis Group.
Forrester, P., Kazumi, U., Soriano, H., Garza, J., & Cruz, L. (2010). Lean production, market share and value creation in the agricultural machinery sector in Brazil. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 21(7), 853-871. DOI: 10.1108/17410381011077955.
Gonzalez, F., Huaman, V., Sotelo, F., & Ramos, E. (2020). Applying Lean Agriculture in Organic Apple Production: Case Study in Peru. Human Interaction, Emerging Technologies and Future Applications IHIET. Paris: Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer.
Hartman, B. (2015). The Lean Farm: How to minimize waste, increase efficiency an maximize value and profits with less work. Chelsea Green.
Hoseini, M., Cocco, S., Casucci, C., Cardelli, V., & Corti, G. (2021). Coffee by products derived: A review. Biomass and Bioenergy, 148, 106009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2021.106009.
Hualpa, A., & Rangel, J. (2023). Traceability in the agricultural sector: A review for the period 2017-2022. Agronomia Mesoamericana, 34(2), 51828. DOI: 10.15517/am.v34i2.51828.
Lermen, F., Echeveste, M., Peralta, C., Sonego, M., & Marcon, A. (2018). A framework for selecting lean practices in sustainable product development: The case study of a brazilian agroindustry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 191, 261-272. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.185.
Manrique, S., Sabogal, K., Sotelo, F., & Ramos, E. (2018). Modelo of quality management applied in lean green agriculture methodology: A research in Perú. 18th LACCEI International Multi Conference for Engineering, Education and Technology. Florida, USA: Virtual Eition.
Martins, A., dos Anjos, F., & da Silva, D. (2023). The Lean Farm: Aplication of tools and concepts of lean manufacturing in agropastoral crops. Sustainability, 15(3), 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032597.
Melin, M., & Barth, H. (2018). Lean in swedish agriculture: strategic and operational perspectives. Production Planning & Control, 29(10), 845-855. DOI: 10.1080/09537287.2018.1479784.
Melin, M., & Barth, H. (2020). Value Stream mapping for sustainable change at a Swedish dairy farm. Environment and waste management, 25(1), 130-140. DOI:10.1504/IJEWM.2020.104367.
Parffit, J., Macnaughton, S., & Barthel, M. (2010). Food waste within food supply chains: Quantification and potential for chage to 2050. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Biological Sciencies, 365, 3065-3081. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0126.
Pearce, D., Dora, M., Wesana, J., & Gellynck, X. (2021). Toward sustainable primary production through the application of lean management in South African fruit horticulture. Journal of Cleaner Production, 313, 127815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127815.
Perdana, T., Sadeli, A., Hermiatin, F., & Ginanjar, T. (2019). Lean management in the rice industry: case study at Widasari, Indramayu District. IOP Conf: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing.
Saaty, T. (2008). Relative measurement and its generalization in decision making: Why pairwise comparisons are central in mathematics for the measurement of intangible factors. Royal Spanish Academy of Sciences, 102(2), 251-318. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191825.
Vinicius, L., Mahlmann, L., Giraldo, F., Hofmann, N., Frozza, R., Aldana, S., & Taborda, C. (2018). A model for Lean and Green integration and monitoring for the coffee sector. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 62-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.03.034.
Womack, J., Jones, D., & Roos, D. (1991). The machine that changed the world: The Story of lean production. Harper Collins.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Scientia Agropecuaria

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The authors who publish in this journal accept the following conditions:
a. The authors retain the copyright and assign to the magazine the right of the first publication, with the work registered with the Creative Commons attribution license, which allows third parties to use the published information whenever they mention the authorship of the work and the First publication in this journal.
b. Authors may make other independent and additional contractual arrangements for non-exclusive distribution of the version of the article published in this journal (eg, include it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book) as long as it clearly indicates that the work Was first published in this journal.
c. Authors are encouraged to publish their work on the Internet (for example, on institutional or personal pages) before and during the review and publication process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and a greater and faster dissemination of work Published (see The Effect of Open Access).




