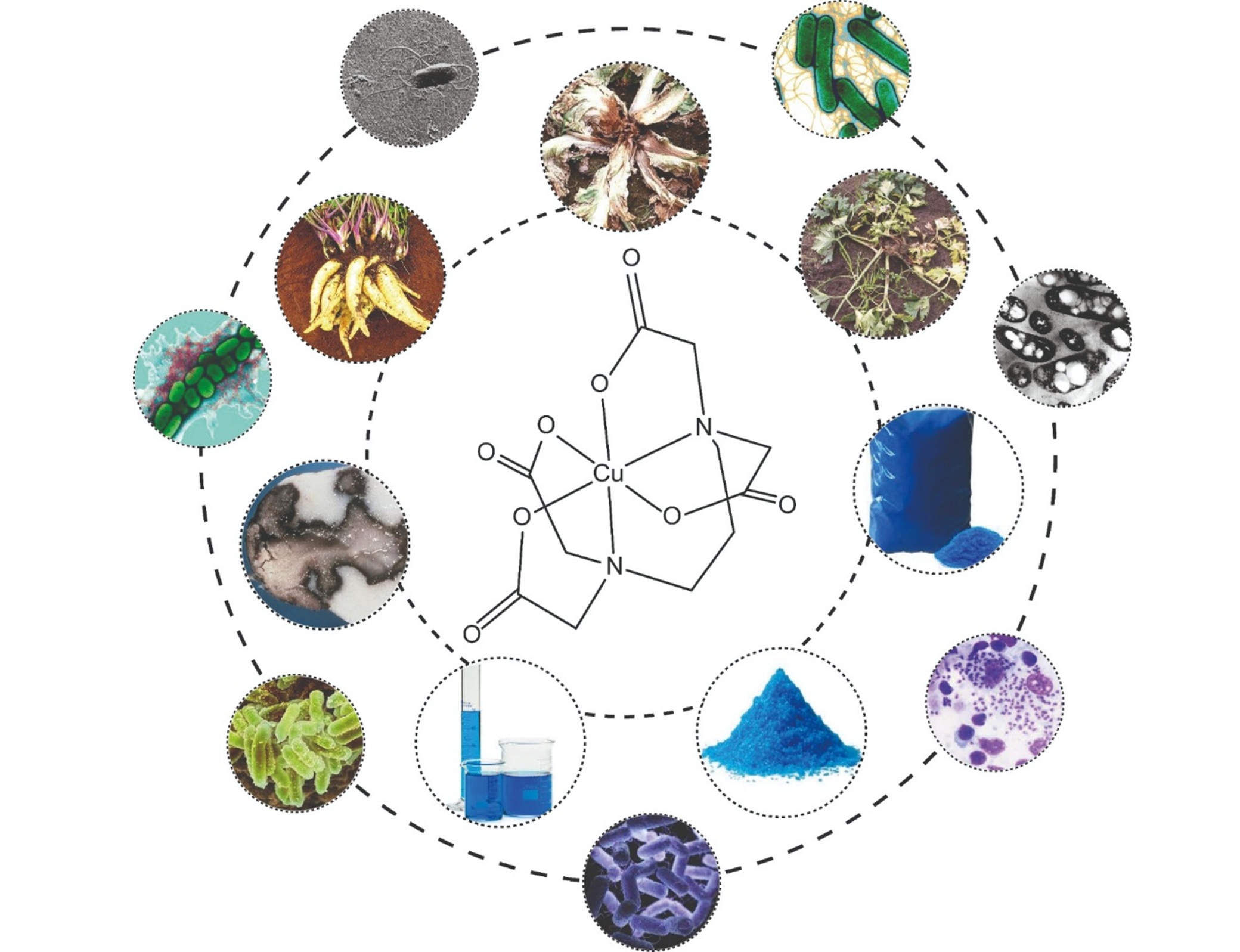
Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of the Cu (II)-1,3-PDTA [(Cu (II) (PDTA)] complex for the control of Erwinia chrysanthemi (soft rot) in the parsley manioc (Arracacia xanthorrhiza Bancroft)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2025.007Palavras-chave:
PDTA, Cu (II), antibiograms, bactericidal activity, new agrochemicalsResumo
Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of the Cu(II)-1,3-PDTA complex was performed by two synthetic routes: sodium and carbonate pathways. The Cu (II)-1,3-PDTA complex can be easily produced by the 1,3-PDTA binder, commercially available as Trilon F (BASF) which is available as sodium or acid salt for the coordination of Cu (II). The biological activity of the Cu (II)-1,3-PDTA [Cu (II)-PDTA] complex was performed to analyze the activity against the bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi Bancroft. The bacterium is the causative agent of soft rot in the parsley maniac (Arracacia xanthorrhiza Bancroft). The bacterium was isolated from parsley manioc infected with soft rot. The metal complex sensitivity tests were performed by diffusion antibiogram. The mean values of the halos and standard deviations of the zones of inhibition were obtained for the [Cu (II) (PDTA)] and Streptomycin complexes. The concentrations of the complexes evaluated were 10-3, 10-2 and 10-1 M (equivalent to 36.3 g L-1 (3.63%), 3.63 g L-1 (0.363%) and 0.363 g L-1 (0.0363%), respectively). The halos were 25.0 ± 1.2 mm for control. For [Cu (II) (PDTA)] complexes, the obtained values were 9.5 ± 0.6, 15.0 ± 0.8 and 24.0 ± 0.8 via sodium and 12.0 ± 1.6, 25.0 ± 0.8 and 31.0 ± 1.9 via carbonate, for 10-3, 10-2 and 10-1 M, respectively. The results showed that the bactericidal activity of the Cu (II)-1,3-PDTA complex obtained by the two synthetic routes are adequate for the control of Erwinia chrysanthemi Bancroft.
Referências
Angelova, V. R., Ivanov, A. S., & Braikov, D. M. (1999). Heavy metals (Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd) in the system soil-grapevine-grape. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 79(5), 713-721. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0010(199904)79:5%3C713::AID-JSFA229%3E3.0.CO;2-F
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, W. M., Sherris, J. C., & Turck, M. (1966). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 45(4), 493-496.
Brun, L. A., Maillet, J., Hinsinger, P., & Pépin, M. (2001). Evaluation of copper availability to plants in copper-contaminated vineyard soils. Environmental Pollution, 111(2), 293-302. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(00)00067-1
Carvalho, C. T., Siqueira, A. B., Rodrigues, E. C., & Ionashiro, M. (2005). Synthesis, characterization and thermal behaviour of solid-state compounds of 2-methoxybenzoate with some bivalent transition metal ions. Eclética Química, 30(4), 19-26. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702005000400003
Chaignon, V., Sanchez-Neira, I., Herrmann, P., Jaillard, B., & Hinsinger, P. (2003). Copper bioavailability and extractability as related to chemical properties of contaminated soils from a vine-growing area. Environmental Pollution, 123(2), 229-238. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00374-3
CLSI - Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. (2006). Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests; Approved standard - 9th ed. CLSI document M2-A9. 26:1. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
Eduah, J. O., Arthur A., Dogbatse, J. A., Amoako-Attah, I., & Afful, E. A. (2024) Ecological effects of soil physicochemical properties and copper speciation on the microbial properties associated with land use management in cacao production. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 33, 103538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2024.103538
Feng, H., Liang, Y. N., & Hu, X. (2022). Natural organic matter (NOM), an underexplored resource for environmental conservation and remediation. Materials Today Sustainability, 19, 100159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100159
Flora, S. J., & Pachauri, V. (2010). Chelation in metal intoxication. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(7), 2745-2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7072745
Gimpel, J., Zhang, H., Davison, W., & Edwards, A. C. (2003). In situ trace metal speciation in lake surface waters using DGT, dialysis, and filtration. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 138-146. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0200995
He, L., Huang, R., Chen, H., Zhao, L., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Discovery and characterization of a novel pathogen Erwinia pyri sp. nov. associated with pear dieback: taxonomic insights and genomic analysis. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15, 1365685. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1365685
Hemathilake, D. M. K. S., & Gunathilake, D. M. C.C. (2022). Agricultural productivity and food supply to meet increased demands. Future Foods: Global Trends, Opportunities, and Sustainability Challenges, 2022, 539-553. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91001-9.00016-5
Jaishankar, M., Tseten, T., Anbalagan, N., Mathew, B. B., & Beeregowda, K. N. (2014). Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7(2), 60-72. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Kagunya, W., Baddour-Hadjean, R., Kooli, F., & Jones, W. (1998) Vibrational modes in layered double hydroxides and their calcined derivatives. Chemical Physics, 236, 225-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0104(98)00234-1
Lakowicz, J. R. (2006). Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. 3rd edition. Springer-Verlag US. 954p. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-46312-4
Madeira, N. R., de Carvalho, A. D. F., da Silva, G. O., Pinheiro, J. B., Pereira, R. B., Michereff Filho, M., Feldberg, N. P., Moreira, S. O., Silveira, G. S. R., & Cássia, R. M. (2017). Proposição de um sistema de produção de mudas de mandioquinha-salsa. Circular Técnica. Brasília, DF.
Martell, A. E., & Smith, R. M. (2001). NIST Critical Constants of Metal Complexes, Version 6.0, Database 46, Gaithersburg, MD, USA.
Martins, P. F. F. (2005). Desenvolvimento de traçadores ativáveis para aplicação em recuperação secundária de reservatórios de Petróleo - Comissão Nacional de Energia Nuclear Centro de Desenvolvimento da Tecnologia Nuclear; Belo Horizonte, MG.
Meylan, S., Odzak, N., Behra, R., & Sigg, L. (2004). Speciation of copper and zinc in natural freshwater: comparison of voltammetric measurements, diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) and chemical equilibrium models. Analytica Chimica Acta, 510(1), 91-100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2003.12.052
Miller, S. A., Ferreira, J. P., & LeJeune, J. T. (2022). Antimicrobial use and resistance in plant agriculture: A one health perspective. Agriculture, 12(2), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12020289
Nakamoto, K. (2009). Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds: Part A: Theory and applications. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470405840
Nóvoa-Muñoz, J. C., Queijeiro, J. M. G., Blanco-Ward, D., Álvarez-Olleros, C., Martínez-Cortizas, A., & García-Rodeja, E. (2007). Total copper content and its distribution in acid vineyards soils developed from granitic rocks. Science of The Total Environment, 378(1-2), 23-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.027
Paterson, J. R., Beecroft, M. S., Mulla, R. S., Osman, D., Reeder, N. L., Caserta, J. A., Young, T. R., Pettigrew, C. A., Davies, G. E., Williams, J. A. G., & Sharples, G. J. (2022). Insights into the antibacterial mechanism of action of chelating agents by selective deprivation of iron, manganese, and zinc. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 88(2), e0164121. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01641-21
Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M., Kriz, G. S., & Vyvyan, J. R. (2010). Introdução à Espectroscopia. 4th ed. Cengage Learning.
Pilgrim, J. (2024). Comparative genomics of a novel Erwinia species associated with the Highland midge (Culicoides impunctatus). Microbial Genomics, 10(4), 2057-5858. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.001242
Pokethitiyook, P., & Poolpak, T. (2016). Biosorption of heavy metal from aqueous solutions Phytoremediation, Springer International Publishing, pp. 113-141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-40148-5_4
Rosa, A. H., Goveia, D., Bellin, I. C., Tonello, P. S., Antunes, M. L. P., Dias Filho, N. L., & Rodrigues Filho, U. P. (2007). Lability study of Cu(II), Cd(II), Mn(II) and Ni(II) complexed by aquatic humic substances using organomodified cellulose membranes. Quimica Nova, 30(1), 59-65. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422007000100014
Sediyama, M. A. N., Vidigal, S. M., Granate, M. J., Santos, M. R., & Mascarenhas, M. H. T. (2005). Cultura da mandioquinha-salsa ou batata-baroa. Belo Horizonte: EPAMIG. 28 p.
Stanojević, I. M., Glišić, B. Đ., Radanović, D. D., & Djuran, M. I. (2021). Copper(II) complexes of aminopolycarboxylate ligands with N2O2, N2O3 and N2O4 donor sets. The relationship between the ligand structure and molecular geometry of the complex, Journal of Molecular Structure, 1232, 130001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130001
Sharma, B., Shukla, S., Rattan, R., Fatima, M., Goel, M., Bhat, M., Dutta, S., Ranjan, R. K., & Sharma, M. (2022). Antimicrobial agents based on metal complexes: Present situation and future prospects. International Journal of Biomaterials, 2022, 6819080. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6819080
Skoog, D. A., West, D. M., Holler, F. J., & Crouch, S. R. (2004). Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry. 8th ed. Thomson/Brooks/Cole – Thomson Learning Belmont, CA, USA, pp. 449-485.
Vašková, J., Stupák, M., Ugurbaş, M. V., Žatko, D, & Vaško, L. (2023). Therapeutic efficiency of humic acids in intoxications. Life, 13(4), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13040971
Wan, Y., Liu, J., Zhuang, Z., Wang, Q., & Li, H. (2024), Heavy metals in agricultural soils: Sources, influencing factors, and remediation strategies. Toxics, 12(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010063
Wang, X., Ma, Y., Hua, L., & McLaughlin, M. J. (2009). Identification of hydroxyl copper toxicity to barley (Hordeum vulgare) root elongation in solution culture. Environmental Toxicology, 28(3), 662-667. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-641.1
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2025 Scientia Agropecuaria

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Los autores que publican en esta revista aceptan los siguientes términos:
a. Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y conceden a la revista el derecho publicación, simultáneamente licenciada bajo una licencia de Creative Commons que permite a otros compartir el trabajo, pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
b. Los autores pueden celebrar acuerdos contractuales adicionales separados para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión publicada de la obra de la revista (por ejemplo, publicarla en un repositorio institucional o publicarla en un libro), pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
c. Se permite y anima a los autores a publicar su trabajo en línea (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de presentación, ya que puede conducir a intercambios productivos, así como una mayor citación del trabajo publicado (ver efecto del acceso abierto).




