El compostaje en agroecología: Efectos sobre la estructura del suelo, la disponibilidad de nutrientes y los microorganismos beneficiosos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2026.015Palabras clave:
Ciclo de nutrientes, Materia orgánica, Resiliencia de cultivos, SostenibilidadResumen
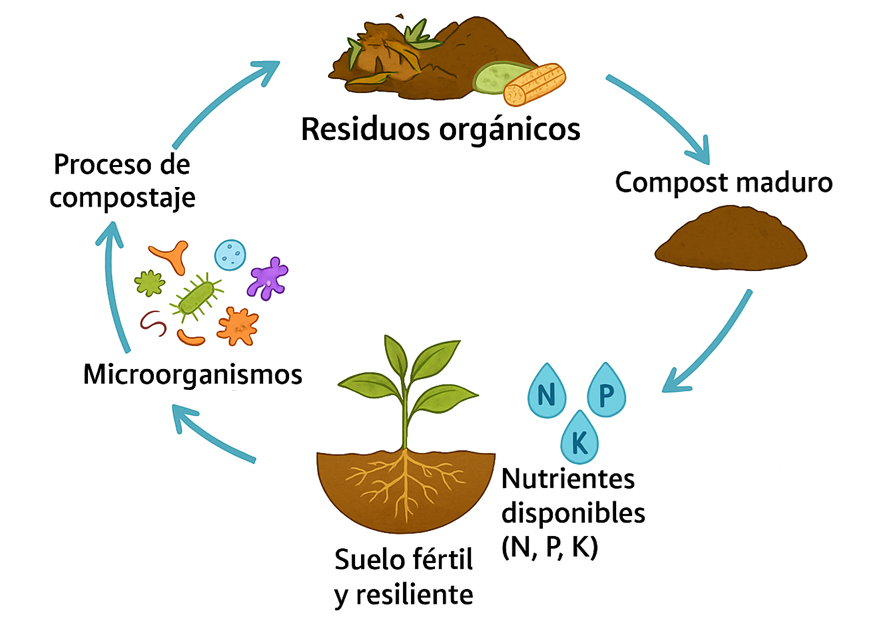
El compostaje es una estrategia clave en la agroecología, que mejora la fertilidad del suelo sin generar efectos negativos en el ambiente. A diferencia de los fertilizantes sintéticos, el compost promueve la regeneración del suelo al incrementar su contenido de materia orgánica, mejorar su estructura y estimular la actividad microbiana beneficiosa. Este artículo de revisión analiza cómo el compostaje optimiza las propiedades físicas, químicas y biológicas del suelo, aumentando su capacidad de retención de agua, la disponibilidad de nutrientes esenciales como nitrógeno, fósforo y potasio, y fortaleciendo la resiliencia de los cultivos frente a enfermedades y estrés ambiental. Se comparan distintos métodos de compostaje, como el vermicompostaje, el compostaje en hileras y el Bokashi, evidenciando que, independientemente del método utilizado, el compost no contribuye a la degradación del suelo, sino que lo enriquece de manera sostenible. Además, se destaca el papel de los microorganismos clave en la mineralización de nutrientes y la mejora del microbioma del suelo, asegurando un suministro equilibrado y de liberación lenta para las plantas. Finalmente, se discuten estrategias innovadoras para optimizar la calidad del compost mediante el uso de inóculos microbianos y enmiendas naturales, consolidando su papel como alternativa sostenible para una producción agrícola eficiente y ambientalmente responsable.
Citas
Andreote, F. D., Gumiere, T., & Durrer, A. (2014). Exploring interactions of plant microbiomes. Scientia Agricola, 71(6), 528–539. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-9016-2014-0195
Ahmed, T., Noman, M., Qi, Y., Shahid, M., Hussain, S., et al. (2023). Fertilization of microbial composts: a technology for improving stress resilience in plants. Plants, 12(20), 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12203550
Ali, A., Jabeen, N., Chachar, Z., Chachar, S., Ahmed, S., Ahmed, N., Laghari, A. A., et al. (2025). The role of biochar in enhancing soil health and interactions with rhizosphere properties and enzyme activities in organic fertilizer substitution. Frontiers in Plant Science, 16, 1595208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2025.1595208
Azim, K., Soudi, B., Boukhari, S., Perissol, C., Roussos, S., & Thami Alami, I. (2018). Composting parameters and compost quality: a literature review. Organic Agriculture, 8(2), 141–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13165-017-0180-z
Naveen, M. (2025). The role of organic matter in soil for improving crop productivity and soil health. Journal of Experimental Agriculture International, 47(2), 367–375. https://doi.org/10.9734/jeai/2025/v47i23296
Castaño, R., Borrero, C., & Avilés, M. (2011). Organic matter fractions by SP-MAS 13C NMR and microbial communities involved in the suppression of Fusarium wilt in organic growth media. Biological Control, 58(3), 286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2011.05.011
Dentel, S. K., & Qi, Y. (2013). Management of sludges, biosolids, and residuals. In Comprehensive Water Quality and Purification (pp. 223–243). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-382182-9.00049-9
El-Ghamry, A. M., El-Sherpiny, M. A., Alkharpotly, A. A., Ghazi, D. A., Helmy, A. A., et al. (2024). The synergistic effects of organic composts and micronutrients on potato growth and productivity under salinity stress. Heliyon, 10(13), e33404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33404
Essel, B., Abaidoo, R. C., Opoku, A., & Ewusi-Mensah, N. (2021). Mechanisms underlying nutrient interaction of compost and mineral fertilizer application in maize (Zea mays L.) cropping system in Ghana. Frontiers in Soil Science, 1, 630851. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoil.2021.630851
Farooq, M. S., Majeed, A., Ghazy, A., Khan, N., Ullah, A., Rehman, A., & Alharby, H. F. (2024). Partial replacement of inorganic fertilizer with organic inputs for enhanced nitrogen use efficiency, grain yield, and decreased nitrogen losses under rice-based systems of mid-latitudes. BMC Plant Biology, 24, 919. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-024-05629-w
Figiel, S., Rusek, P., Ryszko, U., & Brodowska, M. S. (2025). Microbially enhanced biofertilizers: technologies, mechanisms of action, and agricultural applications. Agronomy, 15(5), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051191
Goldan, E., Nedeff, V., Barsan, N., Culea, M., Panainte-Lehadus, M., Mosnegutu, E., Tomozei, C., Chitimus, D., & Irimia, O. (2023). Assessment of manure compost used as soil amendment—A review. Processes, 11(4), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11041167
Gomiero, T., Pimentel, D., & Paoletti, M. G. (2011). Environmental impact of different agricultural management practices: Conventional vs. organic agriculture. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 30(1–2), 95–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2011.554355
Hazman, M., Fawzy, S., Hamdy, A., Abdelkader, A., El-Sayed, A., & Mahmoud, A. (2023). Enhancing rice resilience to drought by applying biochar–compost mixture in low-fertile sandy soil. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 12, 74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-023-00411-7
Ho, T. T. K., Tra, V. T., Le, T. H., Nguyen, N. K. Q., Tran, C. S., et al. (2022). Compost to improve sustainable soil cultivation and crop productivity. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2022.100211
Huang, X., Wang, H., Zou, Y., Qiao, C., Hao, B., Shao, Q., Wu, W., Wu, H., Zhao, J., & Ren, L. (2023). Rice straw composting improves the microbial diversity of paddy soils to stimulate the growth, yield, and grain quality of rice. Sustainability, 15(2), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15020932
Kausar, S., Muhsin, S., Khyber, B., & Azeem, M. (2021). Role of soil microbes in soil health and crop production-a review. Current Research in Agriculture and Farming, 2(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.18782/2582-7146.159
Khanyile, N., Dlamini, N., Masenya, A., Madlala, N. C., & Shezi, S. (2024). Preparation of biofertilizers from banana peels: their impact on soil and crop enhancement. Agriculture, 14(11), 1894. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14111894
Khan, M. S., Zaidi, A., & Ahmad, E. (2014). Mechanism of phosphate solubilization and physiological functions of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. In M. S. Khan, A. Zaidi, & J. Musarrat (Eds.), Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms (pp. 31–62). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-08216-5_2
Kumari, S., Debbarma, R., Habibi, M., Haque, S., & Suprasanna, P. (2025). Banana waste valorisation and the development of biodegradable biofilms. Waste Management Bulletin, 3(3), 100213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wmb.2025.100213
Lerma-Moliz, R., López-González, J. A., Suárez-Estrella, F., Martínez-Gallardo, M. R., Jurado, M. M., et al. (2023). Mitigation of phytotoxic effect of compost by application of optimized aqueous extraction protocols. Science of the Total Environment, 873, 162288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162288
Mago, M., Yadav, A., & Garg, V. K. (2021). Management of banana crop waste biomass using vermicomposting technology. Bioresource Technology, 326, 124742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124742
Martínez-Blanco, J., Lazcano, C., Christensen, T. H., Muñoz, P., Rieradevall, J., Møller, J., Antón, A., & Boldrin, A. (2013). Compost benefits for agriculture evaluated by life cycle assessment: A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 33(4), 721–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0148-7
Mehta, C. M., Palni, U., Franke-Whittle, I. H., & Sharma, A. K. (2014). Compost: Its role, mechanism and impact on reducing soil-borne plant diseases. Waste Management, 34(3), 607–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.11.012
Mekkaoui, F., Ait-El-Mokhtar, M., Zaari Jabri, N., Amghar, I., Essadssi, S., & Hmyene, A. (2024). The Use of Compost and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Their Combination to Improve Tomato Tolerance to Salt Stress. Plants, 13(16), 2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13162225
Mendes, G. O., Dias, C. S., Silva, I. R., Júnior, J. I. R., Pereira, O. L., & Costa, M. D. (2013). Fungal rock phosphate solubilization using sugarcane bagasse. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29(1), 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1156-5
Michel, F., O’Neill, T., Rynk, R., Gilbert, J., Smith, M., Aber, J., & Keener, H. (2022). Forced aeration composting, aerated static pile, and similar methods. In The Composting Handbook (pp. 197–269). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85602-7.00007-8
Nemet, F., Perić, K., & Lončarić, Z. (2021). Microbiological activities in the composting process: A review. Columella: Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, 8(2), 41–53. https://doi.org/10.18380/szie.colum.2021.8.2.41
Nguyen, M. K., Lin, C., Hoang, H. G., Sanderson, P., Dang, B. T., Bui, X. T., Nguyen, N. S. H., Vo, D. V. N., & Tran, H. T. (2022). Evaluate the role of biochar during the organic waste composting process: A critical review. Chemosphere, 299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134488
Ortega-Ramírez, A. T., García Moreno, D., & Reyes Tovar, M. (2024). Composting as a Cleaner Production Strategy for the Soil Resource of Potato Crops in Choconta, Colombia. Resources, 13(10), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13100137
Oueld Lhaj, M., Moussadek, R., Zouahri, A., Sanad, H., Saafadi, L., Mdarhri Alaoui, M., & Mouhir, L. (2024). Sustainable agriculture through agricultural waste management: a comprehensive review of composting’s impact on soil health in moroccan agricultural ecosystems. Agriculture, 14(12), 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122356
Pepe, O., Ventorino, V., & Blaiotta, G. (2013). Dynamic of functional microbial groups during mesophilic composting of agro-industrial wastes and free-living (N2)-fixing bacteria application. Waste Management, 33(7), 1616–1625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.03.025
Rehman, S., De Castro, F., Aprile, A., Benedetti, M., & Fanizzi, F. P. (2023). Vermicompost: Enhancing plant growth and combating abiotic and biotic stress. Agronomy, 13(4), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041134
Rittl, T. F., Grønmyr, F., Bakken, I., & Løes, A. K. (2023). Effects of organic amendments and cover crops on soil characteristics and potato yields. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B — Soil & Plant Science, 73(1), 13–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2023.2165963
Sánchez, O. J., Ospina, D. A., & Montoya, S. (2017). Compost supplementation with nutrients and microorganisms in composting process. Waste Management, 69, 136–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.012
Singh, S., & Nain, L. (2014). Microorganisms in the conversion of agricultural wastes to compost. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy, 80(2), 473. https://doi.org/10.16943/ptinsa/2014/v80i2/4
Soobhany, N. (2018). Preliminary evaluation of pathogenic bacteria loading on organic Municipal Solid Waste compost and vermicompost. Journal of Environmental Management, 206, 763–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.11.029
Soobhany, N., Mohee, R., & Garg, V. K. (2015). Experimental process monitoring and potential of Eudrilus eugeniae in the vermicomposting of organic solid waste in Mauritius. Ecological Engineering, 84, 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.08.003
Sreevidya, M., Gopalakrishnan, S., Kudapa, H., & Varshney, R. K. (2016). Exploring plant growth-promotion actinomycetes from vermicompost and rhizosphere soil for yield enhancement in chickpea. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 47(1), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2015.11.030
Suvendran, S., Acevedo, M. F., Smithers, B., Walker, S. J., & Xu, P. (2025). Soil fertility and plant growth enhancement through compost treatments under varied irrigation conditions. Agriculture, 15(7), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070734
Wang, P., Han, S., & Lin, Y. (2022). Role of microbes and microbial dynamics during composting. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Advances in Composting and Vermicomposting Technology (pp. 169–220). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91874-9.00011-5
Xu, P., Shu, L., Yang, Y., Kumar, S., Tripathi, P., et al. (2024). Microbial agents obtained from tomato straw composting effectively promote tomato straw compost maturation and improve compost quality. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 270, 115884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115884
Yao, X., Guo, H., Zhang, K., Zhao, M., Ruan, J., & Chen, J. (2023). Trichoderma and its role in biological control of plant fungal and nematode diseases. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1160551. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1160551
Zapałowska, A., & Jarecki, W. (2024). The impact of using different types of compost on the growth and yield of corn. Sustainability, 16(2), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020511
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 Scientia Agropecuaria

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Los autores que publican en esta revista aceptan los siguientes términos:
a. Los autores conservan los derechos de autor y conceden a la revista el derecho publicación, simultáneamente licenciada bajo una licencia de Creative Commons que permite a otros compartir el trabajo, pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
b. Los autores pueden celebrar acuerdos contractuales adicionales separados para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión publicada de la obra de la revista (por ejemplo, publicarla en un repositorio institucional o publicarla en un libro), pero citando la publicación inicial en esta revista.
c. Se permite y anima a los autores a publicar su trabajo en línea (por ejemplo, en repositorios institucionales o en su sitio web) antes y durante el proceso de presentación, ya que puede conducir a intercambios productivos, así como una mayor citación del trabajo publicado (ver efecto del acceso abierto).




