Supplementation of feed blocks to the basal diet of native forage improves digestibility and ruminal fermentation in late-gestation sheep
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2026.014Keywords:
Batur sheep, digestibility, feed supplement, forage, microbe, rumen-fermentationAbstract
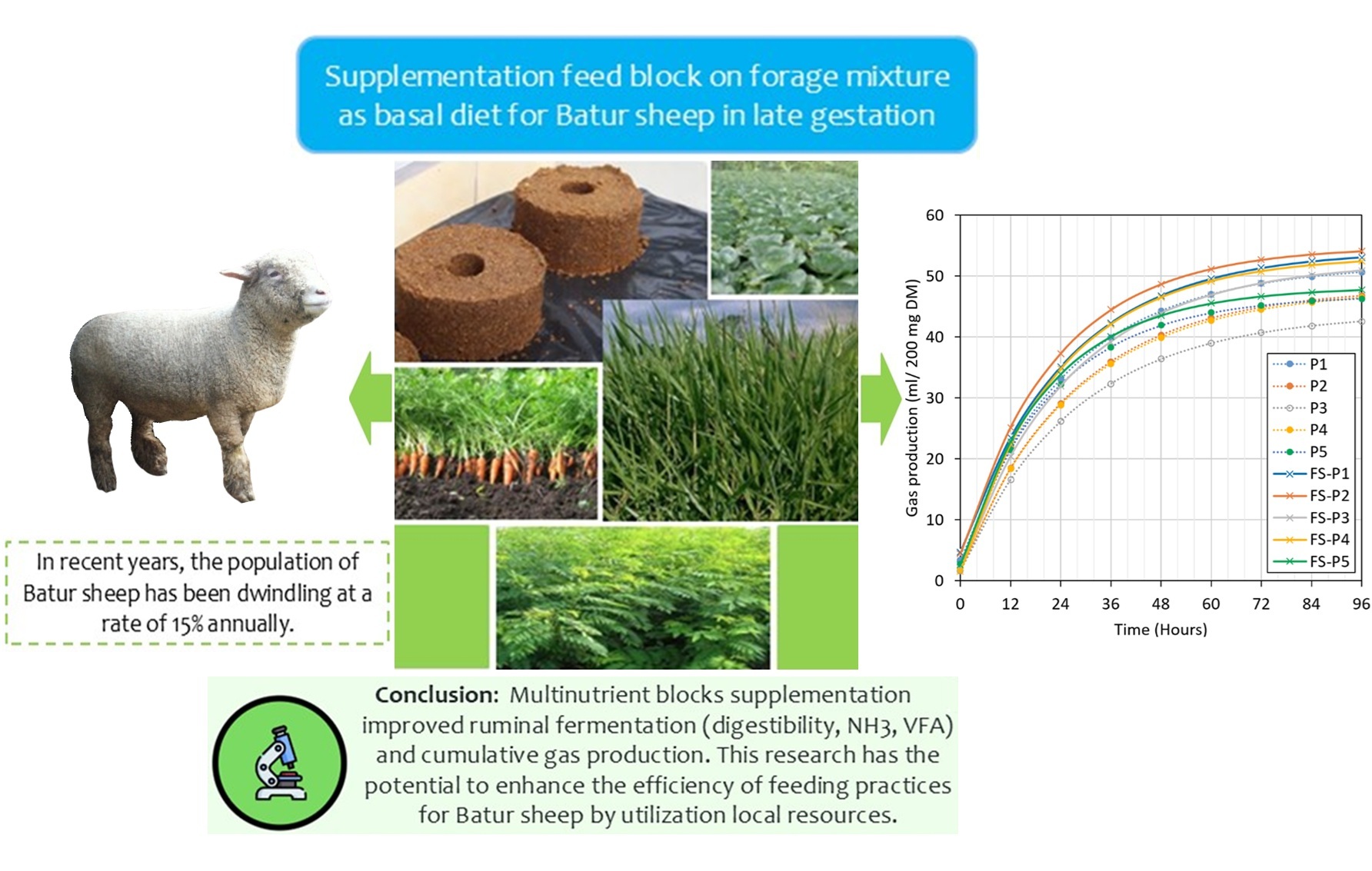
The nutrient content of available native fodders for sheep under tropical conditions is low, while the nutrient requirements of sheep, particularly during late pregnancy, are high. This study aimed to enhance the nutritive value of various indigenous fodders using formulated feed block supplementation to address nutrient insufficiency in late-pregnant crossbred Batur sheep. Five basal diets were formulated from native fodders with and without feed blocks supplementation (FS). Treatments were arranged in a 5 × 2 factorial design, with the first factors being five basal diets and the second factors being supplementation with and without feed block. Each treatment had six replicates. The results showed significant interactions effect (p < 0.01) between the basal diets and supplementation on in vitro digestibility, ruminal pH value, NH3-N, total volatile fatty acids (VFA) concentration, total gas production, total bacterial and protozoa population. The highest response of FS in terms of increased digestibility and total VFA production was observed in the basal diet comprising a 1:1 ratio of dwarf elephant grass and Galinsoga (Galinsoga parviflora) (P4). Feed block supplementation decreased protozoa and bacterial populations in most treatments but tended to increase methane emissions (p = 0.6947). The protozoa population decreased sharply in the P2 basal diet (native grass, carrot leaves, and white hoarypea (Tephrosia candida (Roxb.) DC), while the bacterial population increased significantly in the P4 basal diet. In conclusion, feed block supplementation to native fodder mixture basal diet improves feed digestibility and rumen fermentation to overcome nutrient insufficiency in late-pregnant crossbred Batur sheep.
References
Antari, R., Anggraeny, Y. N., Putri, A. S., Sukmasari, P. K., Krishna N H, Mariyono, M., Aprilliza, M. N., & Ginting, S. (2022). Nutritive and antinutritive contents of Indigofera zollingeriana: Its potency for cattle feed in Indonesia. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 34(2), Article #12.
AOAC. (1995). Official Methods of Analysis. 16th. In Ed. Association of official analytical chemists (Ed.), Science and Education (Washington DC), USA.
Asín, J., Ramírez, G. A., Navarro, M. A., Nyaoke, A. C., Henderson, E. E., Mendonça, F. S., Molín, J., & Uzal, F. A. (2021). Nutritional wasting disorders in sheep. Animals, 11(2), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11020501
Bach, A., Calsamiglia, S., & Stern, M. D. (2005). Nitrogen metabolism in the rumen. Journal of Dairy Science, 88(S), E9–E21. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)73133-7
Baffa, D. F., Oliveira, T. S., Fernandes, A. M., Camilo, M. G., Silva, I. N., Meirelles Júnior, J. R., & Aniceto, E. S. (2023). Evaluation of associative effects of in vitro gas production and fermentation profile caused by variation in ruminant diet constituents. Methane, 2(3), 344–360. https://doi.org/10.3390/methane2030023
Behrendt, R., Hocking Edwards, J. E., Gordon, D., Hyder, M., Kelly, M., et al. (2019). Offering maternal composite ewes higher levels of nutrition from mid-pregnancy to lambing results in predictable increases in birthweight, survival and weaning weight of their lambs. Animal Production Science, 59(10), 1906. https://doi.org/10.1071/AN18505
Chen, L., Dong, Z., Li, J., & Shao, T. (2019). Ensiling characteristics, in vitro rumen fermentation, microbial communities and aerobic stability of low-dry matter silages produced with sweet sorghum and alfalfa mixtures. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(5), 2140–2151. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9406
Conway, E. J., & O’Malley, E. (1942). Microdiffusion methods. Ammonia and urea using buffered absorbents (revised methods for ranges greater than 10μg. N). Biochemical Journal, 36(7–9), 655–661. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj0360655
Costa, M., Alves, S. P., Cappucci, A., Cook, S. R., Duarte, A., Caldeira, R. M., McAllister, T. A., & Bessa, R. J. B. (2018). Effects of condensed and hydrolyzable tannins on rumen metabolism with emphasis on the biohydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66(13), 3367–3377. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04770
Dal Pizzol, J. G., Ribeiro-Filho, H. M. N., Quereuil, A., Le Morvan, A., & Niderkorn, V. (2017). Complementarities between grasses and forage legumes from temperate and subtropical areas on in vitro rumen fermentation characteristics. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 228, 178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.04.020
Delgadillo, J. A., Lemière, A., Flores, J. A., Bedos, M., Hernández, H., et al. (2020). Undernutrition reduces the body weight and testicular size of bucks exposed to long days but not their ability to stimulate reproduction of seasonally anestrous goats. Animal, 14(12), 2562–2569. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731120001329
Department of Agriculture Fisheries and Animal Husbandry. (2019). Hasil Rekapitulasi Pendataan Domba Batur (In English: The Recapitulation Results of Batur Sheep Data). Department of Agriculture Fisheries and Animal Husbandry, Banjarnegara, Indonesia.
Díaz Carrasco, J. M., Cabral, C., Redondo, L. M., Pin Viso, N. D., Colombatto, D., Farber, M. D., & Fernández Miyakawa, M. E. (2017). Impact of chestnut and quebracho tannins on rumen microbiota of bovines. BioMed Research International, Article ID 9610810. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9610810
Gemeda, B. S., & Hassen, A. (2015). Methane production of two roughage and total mixed ration as influenced by cellulase and xylanase enzyme addition. Scientia Agricola, 72(1), 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-9016-2014-0155
Genfors, E., Magnusson, U., Moliso, M. M., Wieland, B., König, U., Hallenberg, G. S., & Båge, R. (2023). Preventive herd management practices and their effect on lamb mortality in Ethiopia. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 55(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-022-03361-x
Gunun, P., Cherdthong, A., Khejornsart, P., Wanapat, M., Polyorach, S., Kang, S., Kaewwongsa, W., & Gunun, N. (2022). The Effect of Phytonutrients in Terminalia chebula Retz. on rumen fermentation efficiency, nitrogen utilization, and protozoal population in goats. Animals, 12(16), 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12162022
Gunun, P., Gunun, N., Khejornsart, P., Ouppamong, T., Cherdthong, A., et al. (2019). Effects of Antidesma thwaitesianum Muell. Arg. pomace as a source of plant secondary compounds on digestibility, rumen environment, hematology, and milk production in dairy cows. Animal Science Journal, 90(3), 372–381. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.13147
Hailemariam, S., Zhao, S., He, Y., & Wang, J. (2021). Urea transport and hydrolysis in the rumen: A review. Animal Nutrition, 7(4), 989–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2021.07.002
Hanoğlu Oral, H., & Yıldız, F. (2025). Structural characteristics of small ruminant production in Muş, Türkiye: A model for organic livestock on the basis of sustainability. Sustainability, 17(7), 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073019
Hartadi, H., Reksohadiprodjo, S., Lebdosukojo, S., Tilman, A. D., Kearl, L. C., & Harris, L. E. (1980). Tables of Feed Composition for Indonesia. International Feedstuffs Institute Utah Agricultural Experiment Station, Utah State University Logan.
Ibrahim, A., Budisatria, I. G. S., Widayanti, R., Atmoko, B. A., Yuniawan, R., & Artama, W. T. (2020). On-farm body measurements and evaluation of Batur sheep on different age and sex in Banjarnegara Regency, Indonesia. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 8(10), 1028-1033. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.aavs/2020/8.10.1028.1033
Idamokoro, E. M., & Masika, P. J. (2017). Peri- and post-parturient consequences of maternal undernutrition of free ranging does: A review. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 29(10), 202.
Kelln, B. M., Penner, G. B., Acharya, S. N., McAllister, T. A., & Lardner, H. A. (2021). Impact of condensed tannin-containing legumes on ruminal fermentation, nutrition, and performance in ruminants: a review. Canadian Journal of Animal Science, 101(2), 210–223. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjas-2020-0096
Khalili, H. (1993). Supplementation of grass hay with molasses in crossbred (Bos taurus × Bos indicus) non-lactating cows: effect of level of molasses on feed intake, digestion, rumen fermentation and rumen digesta pool size. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 41(1), 23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8401(93)90092-X
Kholif, A. E. (2023). A Review of Effect of saponins on ruminal fermentation, health and performance of ruminants. Veterinary Sciences, 10(7), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070450
Khotijah, L., Arofah, N., Erlangga, K., Wijaya, S. H., Diapari, D., Komalasari, K., & Astuti, D. A. (2022). Reproductive performance of ewes, fed flushing diet at different management feeding program. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 25(9), 827-834. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2022.827.834
Kim, H., Kim, B.-W., Yoo, D., Moon, J., Kwon, I., Lee, Y., & Seo, J. (2023). In vitro evaluation of Aloe saponaria as a potential feed additive to modulate ruminal fermentation and microbial diversity. Journal of Applied Animal Research, 51(1), 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2023.2165086
Lang, X., Yang, M., Saleem, A. M., Zhao, X., Xu, H., et al. (2022). Nutritional value, fermentation characteristics and in vitro degradability of whole wheat hay harvested at three stages of Maturity. Animals, 12(11), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111466
Lanzas, C., Sniffen, C. J., Seo, S., Tedeschi, L. O., & Fox, D. G. (2007). A revised CNCPS feed carbohydrate fractionation scheme for formulating rations for ruminants. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 136(3–4), 167–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2006.08.025
Liu, Y., Ma, T., Chen, D., Zhang, N., Si, B., Deng, K., Tu, Y., & Diao, Q. (2019). Effects of tea saponin supplementation on nutrient digestibility, methanogenesis, and ruminal microbial flora in dorper crossbred ewe. Animals, 9(29), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9010029
McDonald, P., Edwards, R. A., Greenhalgh, J. F. D., Morgan, C. A., Sinclair, L. A., & Wilkinson, R. G. (2022). Animal Nutrition (8th edition). Pearson, Harlow, United Kingdom. 2022; p. 159–200.
Mobashar, M., Khan, M. T., Marjan, M., Ahmad, S., Farooq, U., et al. (2023). Urea molasses mineral block under various feeding systems improved nutrient digestibility, productive performance and blood biochemical profile of Yaks. BMC Veterinary Research, 19(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-023-03676-3
Muetzel, S. (2003). Supplementation of barley straw with Sesbania pachycarpa leaves in vitro : effects on fermentation variables and rumen microbial population structure quantified by ribosomal RNA-targeted probes. British Journal of Nutrition, 89(4), 445–453. https://doi.org/10.1079/BJN2002813
Murillo-Ortiz, M., Herrera-Torres, E., Paez-Lerma, J., Ruiz, Ó., Corral-Luna, A., & Pámanes-Carrasco, G. (2019). Digestive and fermentative dynamics in steers supplemented with multi-nutrients blocks containing fermented Opuntia ficus-indica. Animal Nutrition and Feed Technology, 19(3), 395. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-181X.2019.00037.4
Nurjannah, S., Rahman, & Krisnan, R. (2022). Digestibility of Calliandra, Indigofera sp. and the mixture in the ration as a substitute for the concentrate given to the Tup Garut. Proceedings of the International Conference on Improving Tropical Animal Production for Food Security (ITAPS 2021), 20. https://doi.org/10.2991/absr.k.220309.049
Nurlatifah, A., Khotijah, L., Arifiantini, R. I., Maidin, M. S., & Astuti, D. A. (2022). Colostrum quality of ewe fed flushing diet containing EPA and DHA associated with lamb performance. Tropical Animal Science Journal, 45(3), 348–355. https://doi.org/10.5398/tasj.2022.45.3.348
Oginomoto, K., & Imai, S. (1981). Atlas of Rumen Microbiology (S. Imai, Ed.). Japan Scientific Societies Press, Madison, US. 1981; pp1-231
Oliveira, L. E. C., Oliveira, F. H. T., Silva, G. G. C., Bezerra, M. G. S., Morais, É. G., et al. (2022). Nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer application to Elephant gras (Cenchrus purpureus syn. Pennisetum purpureum) cultivar ‘Cameroon’ in an arenosol in Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. Tropical Grasslands-Forrajes Tropicales, 10(3), 280–287. https://doi.org/10.17138/tgft(10)280-287
Ørskov, E. R., & McDonald, I. (1979). The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighted according to rate of passage. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 92(2), 499–503. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600063048
Osman, O. A., Elkhair, N. M., & Abdoun, K. A. (2020). Effects of dietary supplementation with different concentration of molasses on growth performance, blood metabolites and rumen fermentation indices of Nubian goats. BMC Veterinary Research, 16(1), 411. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-020-02636-5
Patra, A. K., & Saxena, J. (2011). Exploitation of dietary tannins to improve rumen metabolism and ruminant nutrition. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 91(1), 24-37. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4152
Peñagaricano, F., Wang, X., Rosa, G. J., Radunz, A. E., & Khatib, H. (2014). Maternal nutrition induces gene expression changes in fetal muscle and adipose tissues in sheep. BMC Genomics, 15(1), 1034. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1034
Prayitno, P., Hartatik, T., Pratiwi, R., & Artama, W. T. (2008). Genetic relatedness between batur, merino and local sheep based on random amplyfied polymorphism DNA marker. Animal Production, 13(1), 2541–5875.
Raffrenato, E., Fievisohn, R., Cotanch, K. W., Grant, R. J., Chase, L. E., & Van Amburgh, M. E. (2017). Effect of lignin linkages with other plant cell wall components on in vitro and in vivo neutral detergent fiber digestibility and rate of digestion of grass forages. Journal of Dairy Science, 100(10), 8119–8131. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-12364
Ramos, J. P. D. F., Sousa, W. H. de, Cavalcante, I. T. R., Oliveira, J. S., Santos, E. M., Pimenta Filho, E. C., Freitas, F. F. de, & Leite, R. M. (2019). Multinutritional blocks as a food strategy to optimize the use of concentrate for lactating goats. Acta Scientiarum. Animal Sciences, 41(1), 47441. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascianimsci.v41i1.47441
Riaz, M. Q., Südekum, K.-H., Clauss, M., & Jayanegara, A. (2014). Voluntary feed intake and digestibility of four domestic ruminant species as influenced by dietary constituents: A meta-analysis. Livestock Science, 162(1), 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2014.01.009
Roberti, S. L., Higa, R., White, V., Powell, T. L., Jansson, T., & Jawerbaum, A. (2018). Critical role of mTOR, PPARγ and PPARδ signaling in regulating early pregnancy decidual function, embryo viability and feto-placental growth. Molecular Human Reproduction, 24(6), 327–340. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gay013
Salami, S. A., Valenti, B., Bella, M., O ’ Grady, M. N., Luciano, G., Kerry, J. P., Jones, E., Priolo, A., & Newbold, C. J. (2018). Characterization of the ruminal fermentation and microbiome in lambs supplemented with hydrolysable and condensed tannins. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 94(5). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy061
Sankar, V., Singh, P., Patil, A. K., Verma, A. K., & Das, A. (2020). Effect of feeding solid multi-nutrient blocks on feed intake, nutrient utilization and haemato-biochemical profile of Crossbred Calves. Indian Journal of Animal Research, 55(12), 1461–1467. https://doi.org/10.18805/IJAR.B-4210
Schoonmaker, J., & Eastridge, M. (2013). Effect of maternal nutrition on calf health and growth. Proceedings of the 22nd Tri-State Dairy Nutrition Conference, Fort Wayne, Indiana, USA. 2013; p. 63–80.
Schwab, C. G., & Broderick, G. A. (2017). A 100-Year Review: Protein and amino acid nutrition in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 100(12), 10094–10112. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13320
Silva, N. C. Da, Cabral Filho, S. L. S., Santos, R. S. Dos, Silva, C. J. Da, Cardoso, R. B., Silva, B. D. M., & Ribeiro, M. D. (2024). Supplementation strategies for ewes during gestation and lactation. Anais Da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 96(suppl 1), e20230686. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202420230686
Silva de Sant’ana, A., Ribeiro Silva, A. P., Oliveira do Nascimento, S. P., Araújo Moraes, A., Fonseca Nogueira, J., et al. (2022). Tannin as a modulator of rumen microbial profile, apparent digestibility and ingestive behavior of lactating goats: A preliminary metagenomic view of goats adaptability to tannin. Research in Veterinary Science, 145, 159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.02.002
Suharlina, S., Astuti, D. A., Nahrowi, N., Jayanegara, A., & Abdullah, L. (2016). In vitro evaluation of concentrate feed containing Indigofera zollingeriana in goat. Journal of the Indonesian Tropical Animal Agriculture, 41(4), 196-203. https://doi.org/10.14710/jitaa.41.4.196-203
Theodorou, M., & Brooks, A. (1990). Evaluation of A New Laboratory Procedure for Estimating the Fermentation Kinetics of Tropical Feeds. In Annual Report. Meidenhead (GB).
Tresia, G. E., Zuratih, Z., & Tiesnamurti, B. (2021). Study of feed accessibility and prospects of horticultural land use in Banjarnegara district as a source of forage production. Bul. Plasma Nutfah 27(2),113–124.
Tulu, A., Gemechu, T., & Mediksa, T. (2023). Effects of Lablab purpurues and concentrate mixed supplements on reproductive performance and pre-weaning growth of Horro sheep grazing natural pasture in Ethiopia. Veterinary and Animal Science, 19, 100281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vas.2022.100281
van Soest, P. J., Robertson, J. B., & Lewis, B. A. (1991). Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science, 74(10), 3583–3597. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(91)78551-2
Vasta, V., Daghio, M., Cappucci, A., Buccioni, A., Serra, A., Viti, C., & Mele, M. (2019). Invited review: Plant polyphenols and rumen microbiota responsible for fatty acid biohydrogenation, fiber digestion, and methane emission: Experimental evidence and methodological approaches. Journal of Dairy Science, 102(5). https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-14985
Wang, Y., McAllister, T. A., Yanke, L. J., & Cheeke, P. R. (2000). Effect of steroidal saponin from Yucca schidigera extract on ruminal microbes. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 88(5), 887–896. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01054.x
Widodo, S., Shiddieqy, M. I., Wahyono, T., Widiawati, Y., & Muttaqin, Z. (2023). Analysis of correlation between nutrient content, digestibility, and gas production of forages in Indonesia. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 11(11), 1770–1778. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.aavs/2023/11.11.1770.1778
Widyarini, S., Sekar Nagari, F., Hanim, C., Bachruddin, Z., Muhlisin, M., & Mira Yusiati, L. (2021). Effect of Nigella sativa L. as saponin sources on in vitro rumen fermentation, enzyme activity and nutrients digestibility. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 9(12). https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.aavs/2021/9.12.2247.2257
Yang, C., Gao, P., Hou, F., Yan, T., Chang, S., Chen, X., & Wang, Z. (2018). Relationship between chemical composition of native forage and nutrient digestibility by Tibetan sheep on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Animal Science, 96(3), 1140–1149. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/sky002
Yeo, J. M., Kim, C. H., Lee, J. H., Nho, W. G., Lee, S. H., & Kim, W. Y. (2006). An evaluation of condensed molasses solubles (cms) as a source of nitrogen for ruminal microbes in vitro. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 48(4), 513–520. https://doi.org/10.5187/JAST.2006.48.4.513
Zhang, W., Yuan, C., Xu, J., & Yang, X. (2015). Beneficial synergetic effect on gas production during co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and biomass in a vacuum reactor. Bioresource Technology, 183, 255–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.113
Zhao, M., Bu, D., Wang, J., Zhou, X., Zhu, D., Zhang, T., Niu, J., & Ma, L. (2016). Milk production and composition responds to dietary neutral detergent fiber and starch ratio in dairy cows. Animal Science Journal, 87(6), 756–766. https://doi.org/10.1111/asj.12482
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Scientia Agropecuaria

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The authors who publish in this journal accept the following conditions:
a. The authors retain the copyright and assign to the magazine the right of the first publication, with the work registered with the Creative Commons attribution license, which allows third parties to use the published information whenever they mention the authorship of the work and the First publication in this journal.
b. Authors may make other independent and additional contractual arrangements for non-exclusive distribution of the version of the article published in this journal (eg, include it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book) as long as it clearly indicates that the work Was first published in this journal.
c. Authors are encouraged to publish their work on the Internet (for example, on institutional or personal pages) before and during the review and publication process, as it can lead to productive exchanges and a greater and faster dissemination of work Published (see The Effect of Open Access).




